Product
Contact Us
Ion Exchange Resin
Ion exchange is a reversible chemical reaction where dissolved ions are removed from solution and replaced with other ions of the same or similar electrical charge. Not a chemical reactant in and of itself, Ion exchange resin is instead a physical medium that facilitates ion exchange reactions. The resin itself is composed of organic polymers that form a network of hydrocarbons. Throughout the polymer matrix are ion exchange sites, where so-called “functional groups” of either positively-charged ions (cations) or negatively-charged ions (anions) are affixed to the polymer network. These functional groups readily attract ions of an opposing charge.
The geometric shape, size, and structure of ion exchange resins can vary from one type to the next. Most ion exchange systems employ a resin bed consisting of tiny, porous microbeads, though some systems, such as those used for electrodialysis, use a sheet-like mesh resin. Ion exchange resin beads are usually small and spherical, with a radius measuring just 0.25 to 1.25 millimeters in size. Depending upon the application and system design, the resin beads may have a uniform particle size or a Gaussian size distribution. Most applications use gel resin beads, which have a translucent appearance, and offer high capacity and chemical efficiency. Macroporous resins, which are recognizable due to their opaque white or yellow appearance, are typically reserved for demanding conditions, since they have comparatively greater stability and chemical resistance.
The ion exchange resin matrix is formed by cross-linking hydrocarbon chains with one another in a process called polymerization. The cross-linking gives the resin polymer a stronger, more resilient structure and a greater capacity (by volume). While the chemical composition of most IX resins is polystyrene, certain types are manufactured from acrylic (either acrylonitrile or methyl acrylate). The resin polymer then undergoes one or more chemical treatments to bind functional groups to the ion exchange sites located throughout the matrix. These functional groups are what give the ion exchange resin its separation capabilities, and will vary significantly from one type of resin to the next.
The most common compositions include:
Strong acid cation exchange resin
Strong acid cation resin is composed of a polystyrene matrix with a sulphonate (SO3–) functional group that is either charged with sodium ions (Na2+) for softening applications, or hydrogen ions (H+) for demineralization.
Weak acid cation exchange resin
Weak acid cation resin is composed of an acrylic polymer that has been hydrolyzed with either sulphuric acid or caustic soda to produce carboxylic acid functional groups. Due to their high affinity for hydrogen ions (H+), Weak acid cation resins are typically used to selectively remove cations associated with alkalinity.
Strong base anion exchange resin
Strong base anion resin is typically composed of a polystyrene matrix that has undergone chloromethylation and amination to fix anions to exchange sites. Type 1 Strong base anion resins are produced by the application of trimethylamine, which yields chloride ions (Cl–), while Type 2 Strong base anion resins are produced by the application of dimethylethanolamine, which yields hydroxide ions (OH–).
Weak base anion exchange resin
Weak base anion resin is typically composed of a polystyrene matrix that has undergone chloromethylation, followed by amination with dimethylamine. Weak base anion resins are unique in that they do not have exchangeable ions, and are therefore used as acid absorbers to remove anions associated with strong mineral acids.
Chelating resin
Chelating resin is the most common type of specialty resin, and are used for selective removal of certain metals and other substances. In most cases the resin matrix is composed of polystyrene, though a variety of substances are used for functional groups, including thiol, triethylammonium, and aminophosphonic, among many others.
Mixed bed resin(DI Resin)
Mixed bed resin(DI Resin) is composed of gel-type strong acid cation exchange resin and gel type strong basic anion exchange resin. It is suitable for the preparation and refining of ultra-pure water. It is widely used in water fields such as electronics, optical instruments, medicine, cosmetics, window cleaning and precision machining.
Mixed bed resin(DI Resin) has excellent kinetics and exchange capacity, high purification purity and regeneration level, excellent physicochemical stability and penetration resistance.
High purity water can be produced with resistivity more than 15MΩ.cm.
Cation Exchange Resin
|
SeeChee Model |
Functional Groups |
Ionic form |
Mass exchange Capacity (mmol/g) |
Volume exchange Capacity (mmol/ml) |
Particle size Range % (0.315-1.25mm) |
Moisture Content % |
Bulk Density (g/ml) |
Sphericity after Attrition % |
Reversible swelling % |
PH range |
|
001×4 |
-SO3H |
Na |
≥ 4.5 |
≥ 1.3 |
≥ 95% |
55.0-65.0 |
0.74-0.84 |
≥ 90% |
Na→H 22-25 |
1-14 |
|
001×7 |
-SO3H |
Na |
≥ 4.5 |
≥ 1.9 |
≥ 95% |
45.0-50.0 |
0.77-0.87 |
≥ 90% |
Na→H ≤ 10 |
1-14 |
|
001×8 |
-SO3H |
Na |
≥ 4.5 |
≥ 2.0 |
≥ 95% |
42.0-48.0 |
0.78-0.88 |
≥ 95% |
Na→H 7-9 |
1-14 |
|
001×10 |
-SO3H |
Na |
≥ 4.3 |
≥ 2.2 |
≥ 95% |
38.0-45.0 |
0.82-0.92 |
≥ 90% |
Na→H 3-5 |
1-14 |
|
D001 |
-SO3H |
Na |
≥ 4.35 |
≥ 1.80 |
≥ 95 |
45.0-55.0 |
0.77-0.85 |
≥ 90% |
Na→H 9-10 |
1-14 |
|
110 |
-COOH |
Na H |
≥ 12.0(H) |
≥ 4.0(H) |
≥ 95% |
52-62(H) |
0.68-0.82(H) |
≥ 70 |
H→Na 70-75 |
5-14 |
|
D113 |
-COOH |
H |
≥ 10.8(H) |
≥ 4.4(H) |
≥ 95% |
45-52 |
0.72-0.80 |
≥ 90% |
H→Na ≤ 70 |
4-14 |
|
D152 |
-COOH |
Na |
≥ 8.0(H) |
≥ 2.0(H) |
≥ 90% |
60-70 |
0.70-0.80 |
≥ 90% |
H→Na 75-80 |
4-14 |
Anion Exchange Resin
|
SeeChee Model |
Functional Groups |
Ionic form |
Mass exchange Capacity (mmol/g) |
Volume exchange Capacity (mmol/ml) |
Particle size Range % (0.315-1.25mm) |
Moisture Content % |
Bulk Density (g/ml) |
Sphericity after Attrition % |
Reversible swelling % |
PH range |
|
201×4 |
-N+(CH3)3 |
Cl |
≥ 3.7 |
≥ 1.10 |
≥ 95% |
50-60 |
0.66-0.71 |
≥ 90% |
Cl→OH 25-30 |
1-14 |
|
201×7 |
-N+(CH3)3 |
Cl |
≥ 3.5 |
≥ 1.35 |
≥ 95% |
42-48 |
0.67-0.73 |
≥ 90% |
Cl→OH 18-22 |
1-14 |
|
D201 |
-N+(CH3)3 |
Cl |
≥ 3.7 |
≥ 1.2 |
≥ 95% |
50-60 |
0.65-0.73 |
≥ 90% |
Cl→OH ≤ 20 |
1-14 |
|
D202 |
-N+(CH3)2C2H4OH3H |
Cl |
≥ 3.6 |
≥ 1.2 |
≥ 95% |
47-57 |
0.68-0.74 |
≥ 90% |
Cl→OH ≤ 20 |
1-14 |
|
D301 |
-N(CH3)2 |
Free Base |
≥ 4.8 |
≥ 1.45 |
≥ 95% |
48-58 |
0.65-0.72 |
≥ 90% |
Cl→OH ≤ 28 |
1-9 |
|
D301G |
-N(CH3)2 |
OH- |
≥ 4.2 |
≥ 1.3 |
0.60-1.50mm ≥ 95 |
50-60 |
0.65-0.72 |
≥ 95% |
Cl→OH ≤ 28 |
1-9 |
|
D311 |
-NH2 |
Free Base |
≥ 7.0 |
≥ 2.2 |
≥ 95% |
55-65 |
0.70-0.80 |
≥ 95 |
OH→Cl ≤ 25 |
1-9 |
Food Grade Ion Exchange Resin
|
SeeChee Model |
Functional Groups |
Ionic form |
Mass exchange Capacity (mmol/g) |
Volume exchange Capacity (mmol/ml) |
Particle size Range % (0.315-1.25mm) |
Moisture Content % |
Bulk Density (g/ml) |
Sphericity after Attrition % |
Reversible swelling % |
PH range |
|
001×4 |
-SO3H |
Na |
≥ 4.5 |
≥ 1.3 |
≥ 95% |
55.0-65.0 |
0.74-0.84 |
≥ 95% |
Na→H 22-25 |
1-14 |
|
001×7 |
-SO3H |
Na |
≥ 4.5 |
≥ 1.9 |
≥ 95% |
45.0-50.0 |
0.77-0.87 |
≥ 95% |
Na→ H ≤ 10 |
1-14 |
|
001×8 |
-SO3H |
Na |
≥ 4.5 |
≥ 2.0 |
≥ 95% |
42.0-48.0 |
0.78-0.88 |
≥ 95% |
Na→H 7-9 |
1-14 |
|
001×10 |
-SO3H |
Na |
≥ 4.2 |
≥ 2.2 |
≥ 95% |
38.0-45.0 |
0.82-0.92 |
≥ 95% |
Na→H 3-5 |
1-14 |
|
D113 |
-COOH |
H |
≥ 10.8(H) |
≥ 4.4(H) |
≥ 95% |
45-52 |
0.72-0.80 |
≥ 95% |
H→Na ≤ 70 |
4-14 |
Mixed Bed Resin
|
SeeChee Model |
Functional Groups |
Ionic form |
Volume exchange Capacity (mmol/ml) |
Moisture Content % |
Bulk Density (g/ml) |
Particle size Range % (0.315-1.25mm) |
PH range |
|
MB300 |
001×7H:50% 201×7OH:50% |
Cation:≥ 99% H Anion:≥ 90% OH |
0.5 |
50-60 |
0.72-0.76 |
≥ 95% |
1-14 |
|
MB400 |
001×7H:40% 201×7OH:60% |
Cation:≥ 99% H Anion:≥ 90% OH |
0.6 |
50-60 |
0.71-0.74 |
≥ 95% |
1-14 |
SeeChee Closest Competitive Equivalents
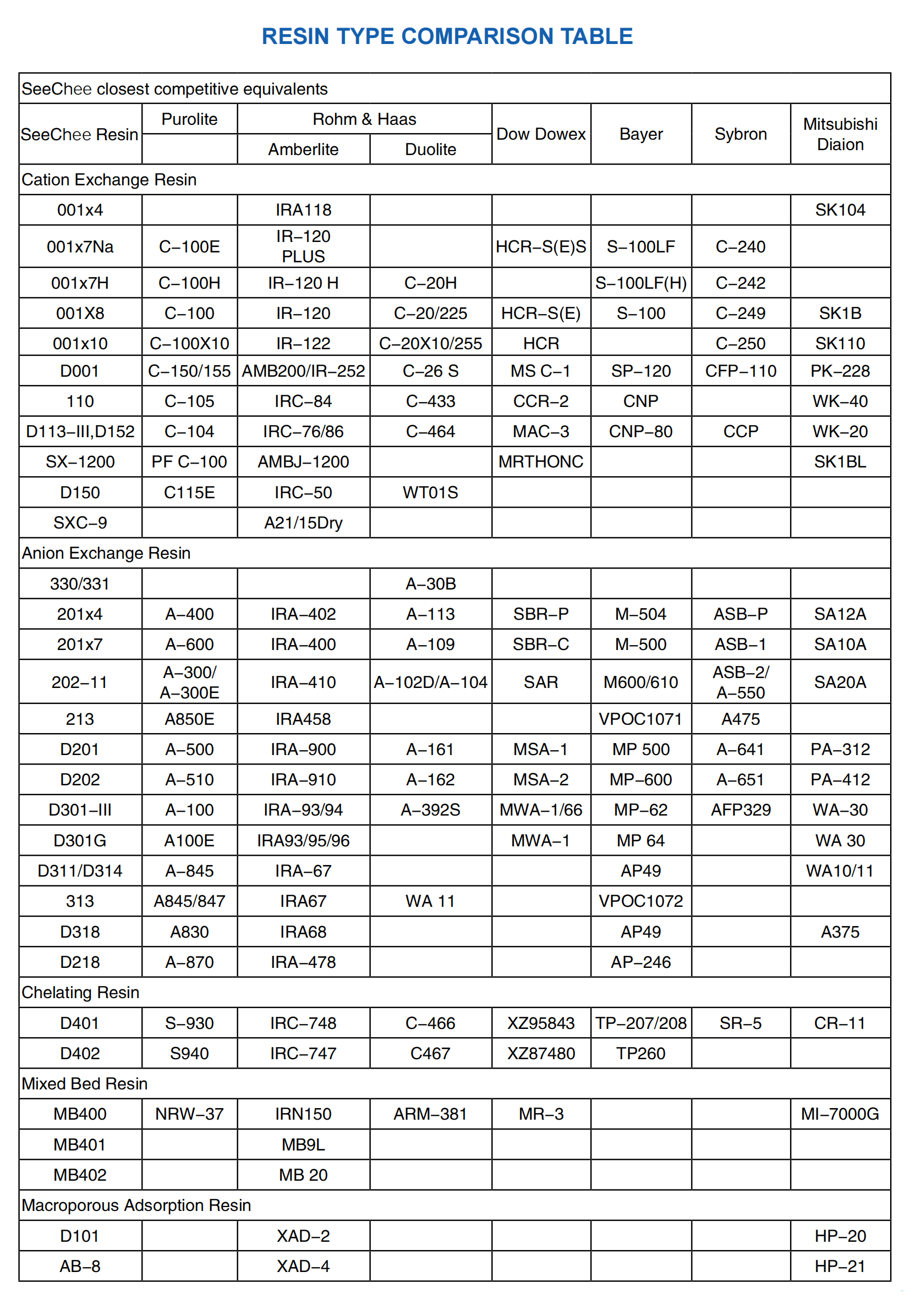
Product Show




